Ensuring an efficient, equitable & cohesive territory
Paraguay
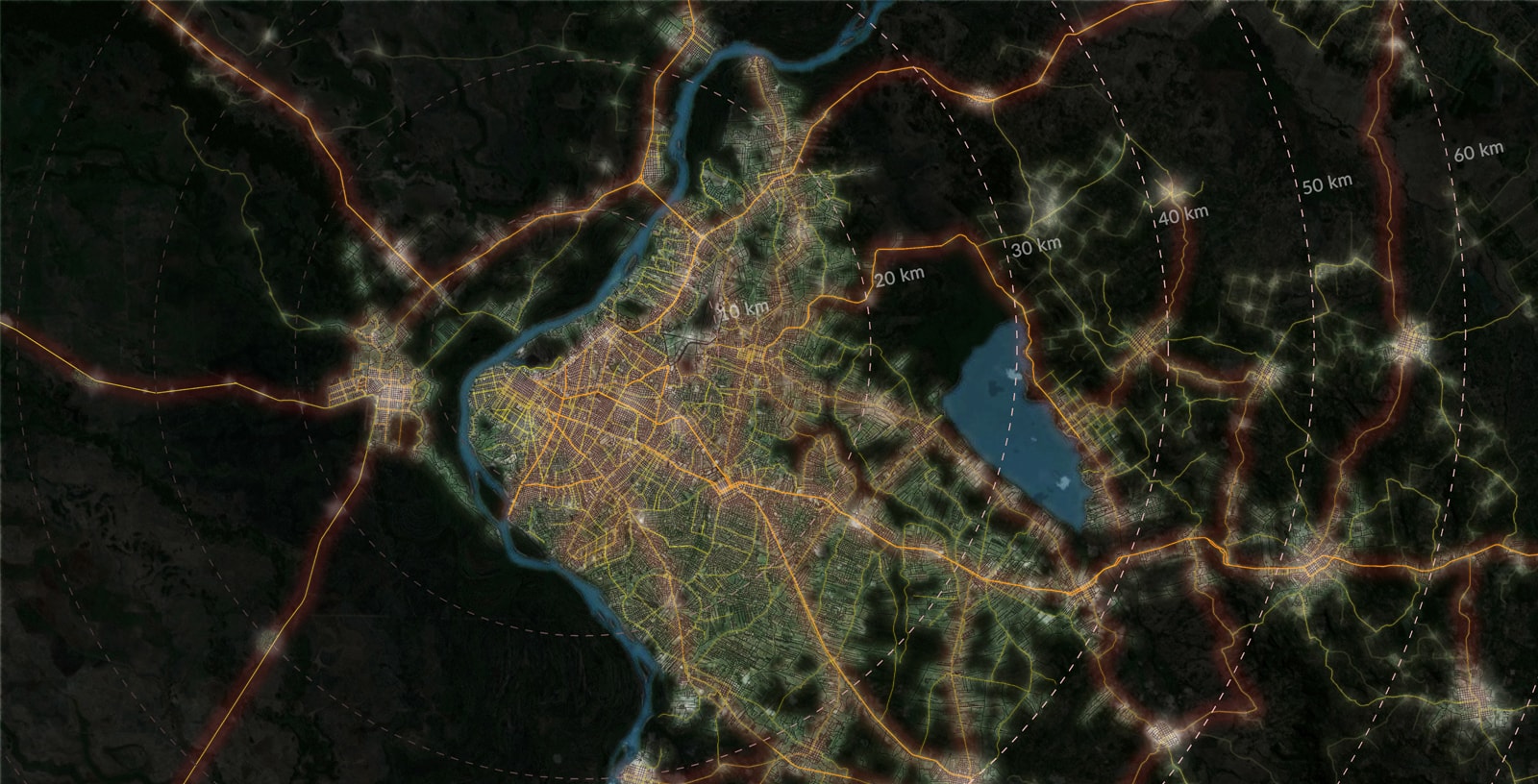
Asuncion, Paraguay’s capital, is head of a metropolis with almost 3 million inhabitants in a territory that spans over 1,500 km2. In recent decades, its accelerated and unplanned expansion has generated a disperse and low-density territory, where urban settlements have invaded environmentally vulnerable areas offering low quality of life due to the lack of accessibility and infrastructure, urban services, facilities and decent housing. IDOM, in collaboration with the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB) has carried out an analysis and diagnosis to address the most urgent challenges on sustainability and propose specific actions to rectify current trends.
Más información
Implementing measures which enable an optimal management of existing resources
Asuncion Metropolitan Area (AMA) is still in the process of urbanization which has been intensified during the recent decades, reaching almost a 3.8% annual urban footprint growth and currently taking 65% of Paraguay’s population. This uncontrolled population growth has generated new opportunities, but also huge challenges as regards economic competitiveness of the region and quality of life for the population. IDOM has worked with the key players at a metropolitan and municipal scale and with the IDB to define the basis for a new territorial model which ensures a sustainable development of Asuncion and its area of influence.
In this context, a territorial development plan for the Metropolitan Area of Asuncion is proposed under a Smart Growth Scenario to 2030 and 2050, setting up the optimal urban growth scenario, which allows to fix the upper boundary limit for the future development under a perspective of sustainable development. The basic criteria for defining these limits are aimed at improving the quality of life of the population by implementing measures which enable an optimal management of existing resources, such as: densification and compacity of areas suitable for development in order to limit expansion to the periphery; consolidation of the the head municipalities of AMA; reducing the overall cost of investment in water infrastructure, sanitation and drainage, transportation and waste collection; promoting a low-carbon economy through eco-mobility and commitment to public transport and adapting public space to non motorized vehicles. Currently, 36% of the greenhouse gas (GHGs) emissions have its origin in the consumption of transport fuels, predominantly for private vehicles. Also, vulnerable areas to natural hazards are protected, especially towards flooding, to mitigate the impact of seasonal climacteric phenomena in urbanized areas. In addition, land use planning is orientated so as to ensure efficiency, equity and social cohesion.
CLIENT:
Inter-American Development Bank
SCOPE:
Inventory and Diagnosis of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Probabilistic Risk Analysis
Urban Growth Scenarios
Workshop on Public Participation